Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Seiya; Arai, Yoichi; Okamura, Nobuo; Watanabe, Masayuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.839 - 848, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The fuel debris, consisting of nuclear fuel materials and reactor structural materials, generated in the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant can become deteriorated like rocks under the changes of environmental temperature. Although the fuel debris have been cooled by water for 10 years, they are affected by seasonal and/or day-and-night temperature changes. Therefore, in evaluating the aging behavior of the fuel debris, it is essential to consider the changes in environmental temperature. Assuming that the fuel debris are deteriorated, radioactive substances that have recently undergone micronization could be eluted into the cooling water, and such condition may affect defueling methods. We focused on the effect of repeated changes in environmental temperature on the occurrence of cracks, and an accelerated test using simulated fuel debris was carried out. The length of the crack increases with increasing number of heat cycle; therefore, the fuel debris become brittle by stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction. In conclusion, it was confirmed that the mechanical deterioration of the fuel debris is similar to that of rocks or minerals, and it became possible to predict changes in the length of the crack in the simulated fuel debris and environmental model.
Ota, Hirokazu*; Ogata, Takanari*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Futagami, Satoshi; Shimada, Sadae*; Yamada, Yumi*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/05
Maekawa, Fujio; Takei, Hayanori
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 98(5), p.206 - 210, 2022/05
In developing an accelerator-driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS), it is necessary to solve technical issues related to proton beams, such as the development of materials that can withstand high-intensity proton beams and the characterization of subcritical cores driven by proton beams. Therefore, at the high-intensity proton accelerator facility J-PARC, a transmutation experimental facility that actually conducts various tests using a high-intensity proton beam is being planned. This paper introduces the outline and future direction of the transmutation experimental facility.
Gunji, Satoshi; Tonoike, Kotaro; Clavel, J.-B.*; Duhamel, I.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(1), p.51 - 61, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)The new critical assembly STACY will be able to contribute to the validation of criticality calculations related to the fuel debris. The experimental core designs are in progress in the frame of JAEA/IRSN collaboration. This paper presents the method applied to optimize the design of the new STACY core to measure the criticality characteristics of pseudo fuel debris that simulated Molten Core Concrete Interaction (MCCI) of the fuel debris. To ensure that a core configuration is relevant for code validation, it is important to evaluate the reactivity worth of the main isotopes of interest and their k sensitivity to their cross sections. In the case of the fuel debris described in this study, especially for the concrete composition, silicon is the nucleus with the highest k
sensitivity to their cross sections. In the case of the fuel debris described in this study, especially for the concrete composition, silicon is the nucleus with the highest k sensitivity to the cross section. For this purpose, some parameters of the core configuration, as for example the lattice pitches or the core dimensions, were adjusted using optimization algorithm to find efficiently the optimal core configurations to obtain high sensitivity of silicon capture cross section. Based on these results, realistic series of experiments for fuel debris in the new STACY could be defined to obtain an interesting feedback for the MCCI. This methodology is useful to design other experimental conditions of the new STACY.
sensitivity to the cross section. For this purpose, some parameters of the core configuration, as for example the lattice pitches or the core dimensions, were adjusted using optimization algorithm to find efficiently the optimal core configurations to obtain high sensitivity of silicon capture cross section. Based on these results, realistic series of experiments for fuel debris in the new STACY could be defined to obtain an interesting feedback for the MCCI. This methodology is useful to design other experimental conditions of the new STACY.
Hirota, Noriaki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(12), p.1276 - 1286, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influence of materials of mineral-insulated (MI) cables on their electrical characteristics upon exposure to high-temperature conditions was examined via a transmission test, in the objective of achieving the stability of the potential distribution along the cable length. Occurrence of a voltage drop along the cable was confirmed for aluminum oxide (Al O
O ) and magnesium oxide (MgO), as insulating materials of the MI cable. A finite-element method (FEM)-based analysis was performed to evaluate the leakage in the potentials, which was found at the terminal end. Voltage drop yields by the transmission test and the analysis were in good agreement for the MI cable of Al
) and magnesium oxide (MgO), as insulating materials of the MI cable. A finite-element method (FEM)-based analysis was performed to evaluate the leakage in the potentials, which was found at the terminal end. Voltage drop yields by the transmission test and the analysis were in good agreement for the MI cable of Al O
O and MgO materials, which suggests the reproducibility of the magnitude relationship of the experimental results via the FEM analysis. To suppress the voltage drop, the same FEM analysis was conducted, the diameter of the core wires (
and MgO materials, which suggests the reproducibility of the magnitude relationship of the experimental results via the FEM analysis. To suppress the voltage drop, the same FEM analysis was conducted, the diameter of the core wires ( ) and the distance between them (
) and the distance between them ( ) were varied. Considering the variation of
) were varied. Considering the variation of  , the potential distribution in the MI cable produced a minimum voltage drop corresponding to a ratio
, the potential distribution in the MI cable produced a minimum voltage drop corresponding to a ratio 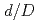 of 0.35, obtained by dividing
of 0.35, obtained by dividing  with that of the insulating material (
with that of the insulating material ( ). In case of varying
). In case of varying  , a minimum voltage drop was l/
, a minimum voltage drop was l/ of 0.5.
of 0.5.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Tojo, Masayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(12), p.1061 - 1062, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Reactor Physics that treat the essentials of how fission nuclear reactors work fundamentally has important roles on safe operations and design studies of various types of nuclear reactors. From the latest activities in the field of reactor physics, this report summarizes some outstanding researches and developments published in scientific journals including the Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology.
Goto, Minoru; Fukaya, Yuji; Mizuta, Naoki; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Yan, X.
Proceedings of 9th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2018/10
The HTTR (High Temperature engineering Test Reactor) constructed at JAEA-Oarai R&D center is a block-type experimental HTGR (High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor) with 30 MW thermal power. It attained the first criticality at 1998 and has yielded very useful data for future HTGR design. Although the HTTR was designed very conservatively because the HTTR is the first HTGR for Japan, future HTGRs can be designed with a reasonable conservativeness based on the HTTR data. Additionally, it is possible to enhance the performance of the reactor core by improving the design and introducing new technologies. This paper describes a concept of an experimental HTGR that is upgraded from the HTTR by the reasonable conservativeness, the design improvement and the new technology introduction.
Sugawara, Takanori; Kita, Satoshi*; Yoshimoto, Hidemitsu*; Okubo, Nariaki
JAEA-Technology 2018-008, 26 Pages, 2018/09
The oxygen sensors to measure the oxygen concentration in liquid LBE (lead-bismuth eutectic) were fabricated and tested for future use in LBE-cooled ADS (accelerator-driven system) or LBE test loops. The following tests were performed; estimation of catalyst application range, freeze seal structure and estimation of gamma-ray irradiation effect. For the estimation of the catalyst application range, it was confirmed that the measurement accuracy became worse in low LBE temperature as the application range became small. For the freeze seal structure, we realized the structure to prevent the LBE leakage with 0.5 MPa pressure condition. For the estimation of gamma-ray irradiation effect, the ex-situ test was carried out and it was observed that there was little effect by 4 MGy gamma-ray irradiation.
Narukawa, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Jang, S.*; Amaya, Masaki
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM-14) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2018/09
Eguchi, Yuta; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Tazawa, Yujiro; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/07
In order to investigate the basic neutronics characteristics of the accelerator-driven subcritical system (ADS), JAEA has a plan to construct a new critical assembly in the J-PARC project, Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P). This study aims to evaluate the natural cooling characteristics of TEF-P core which has large decay heat by minor actinide (MA) fuel, and to achieve a design that does not damage the core and the fuels during the failure of the core cooling system. In the evaluation of the TEF-P core temperature, empty rectangular lattice tube outer of the core has a significant effect on the heat transfer characteristics. The experiments by using the mockup device were performed to validate the heat transfer coefficient and experimental results were obtained. By using the obtained experimental results, the three-dimensional heat transfer analysis of TEF-P core were performed, and the maximum core temperature was obtained, 294 C. This result shows TEF-P core temperature would be less than 327
C. This result shows TEF-P core temperature would be less than 327 C that the design criterion of temperature.
C that the design criterion of temperature.
Maekawa, Fujio; Transmutation Expeimental Facility Design Team
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 13(Sp.1), p.2505045_1 - 2505045_4, 2018/05
The partitioning and transmutation (P-T) technology has promising potential for volume reduction and mitigation of degree of harmfulness of high-level radioactive waste. JAEA is promoting development of the P-T technology by using an accelerator driven system (ADS). To facilitate the development, we have a plan to construct the Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) as one of experimental facilities of J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex). TEF consists of two facilities: the ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) and the Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P). Recent progress in design and R&D efforts toward construction of J-PARC TEF will be presented.
Partitioning and Transmutation Technology Division, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center
JAEA-Technology 2017-033, 383 Pages, 2018/02
JAEA is pursuing research and development (R&D) on volume reduction and mitigation of degree of harmfulness of high-level radioactive waste. Construction of Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) is under planning as one of the second phase facilities in the Japan Proton Accelerator Complex (J-PARC) program to promote R&D on the transmutation technology with using accelerator driven systems (ADS). The TEF consists of two facilities: ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) and Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P). Development of spallation target technology and study on target materials are to be conducted in TEF-T with impinging a high intensity proton beam on a liquid lead-bismuth eutectic target. Whereas in TEF-P, by introducing a proton beam to minor actinide loaded cores, reactor physical properties of the cores are to be studied, and operation experiences of ADS are to be acquired. This report summarizes results of safety design for establishment permit of one of two TEF facilities, TEF-P.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio; Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro
JAEA-Technology 2017-029, 39 Pages, 2018/01
Under an assumption that an incident of lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) leak from an LBE circulation system occurred during a 250-kW beam operation, an estimation of radiation dose at the site boundary for the ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) in Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) of J-PARC was conducted using various conservative assumptions. As a result, the radiation dose at the site boundary was estimated to be about 660  Sv, which were dominated by mercury, noble gas, and iodine produced as spallation products from the LBE. Even though the incident scenario was made conservatively, it was shown that the estimated total dose was lower than the annual radiation dose due to natural sources, and the TEF-T has sufficient safety margin for the leak of radioactivity.
Sv, which were dominated by mercury, noble gas, and iodine produced as spallation products from the LBE. Even though the incident scenario was made conservatively, it was shown that the estimated total dose was lower than the annual radiation dose due to natural sources, and the TEF-T has sufficient safety margin for the leak of radioactivity.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.01016_1 - 01016_9, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)Maekawa, Fujio; Sasa, Toshinobu
Enerugi Rebyu, 37(9), p.15 - 18, 2017/08
Accelerator driven nuclear transmutation systems (ADS) are under development for reducing nuclear waste. The J-PARC Transmutation Experimental Facility program and situation of the world for the ADS development are introduced.
Sasa, Toshinobu; Saito, Shigeru; Obayashi, Hironari; Sugawara, Takanori; Wan, T.; Yamaguchi, Kazushi*; Yoshimoto, Hidemitsu
NEA/CSNI/R(2017)2 (Internet), p.111 - 116, 2017/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) proposes to reduce the environmental impact caused from high-level radioactive waste by using Accelerator-driven system (ADS). To realize ADS, JAEA plans to build the Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) within the framework of J-PARC project. For the JAEA-proposed ADS, lead-bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) is adopted as a coolant for subcritical core and spallation target. By using TEF in J-PARC, we are planning to solve technical difficulties for LBE utilization by completion of the data for the design of ADS. The 250kW LBE spallation target will be located in TEF facility to prepare material irradiation database. Various R&Ds for important technologies required to build the facilities are investigated such as oxygen content control, instruments development, remote handling techniques for target maintenance, and spallation target design. The large scale LBE loops for 250kW target mock up and material corrosion studies are also manufactured and ready for various experiments. The latest status of 250kW LBE spallation target optimization will be described in the presentation.
Nuclear Transmutation Division, J-PARC Center
JAEA-Technology 2017-003, 539 Pages, 2017/03
JAEA is pursuing R&D on volume reduction and mitigation of degree of harmfulness of high-level radioactive waste based on the "Strategic Energy Plan" issued in April 2014. Construction of Transmutation Experimental Facility is under planning as one of the second phase facilities in the J-PARC program to promote R&D on the transmutation technology with using accelerator driven systems (ADS). The TEF consists of two facilities: ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) and Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P). Development of spallation target technology and study on target materials are to be conducted in TEF-T with impinging a high intensity proton beam on a lead-bismuth eutectic target. Whereas in TEF-P, by introducing a proton beam to minor actinide loaded subcritical cores, physical properties of the cores are to be studied, and operation experiences are to be acquired. This report summarizes results of technical design for construction of one of two TEF facilities, TEF-T.
 CEN and JAEA for Partitioning and Transmutation through Accelerator-Driven System
CEN and JAEA for Partitioning and Transmutation through Accelerator-Driven SystemWorking Group for Collaboration between SCK CEN and JAEA for P&T through ADS
CEN and JAEA for P&T through ADS
JAEA-Review 2017-003, 44 Pages, 2017/03
This technical report reviews Research and Development (R&D) programs for the Partitioning and Transmutation (P&T) technology through Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) at Studiecentrum voor Kernenergie/Centre d'Etude de l' nergie Nucl
nergie Nucl aire (SCK
aire (SCK CEN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The results obtained in the present Collaboration Arrangement between the two organizations for the ADS are also summarized, and possible further collaborations and mutual realizations in the future are sketched.
CEN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The results obtained in the present Collaboration Arrangement between the two organizations for the ADS are also summarized, and possible further collaborations and mutual realizations in the future are sketched.
Tazawa, Yujiro; Nishihara, Kenji; Sugawara, Takanori; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sasa, Toshinobu; Eguchi, Yuta; Kikuchi, Masashi*; Inoue, Akira*
JAEA-Technology 2016-029, 52 Pages, 2016/12
Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P) planned in the J-PARC project uses minor actinide (MA) fuels in the experiments. These MA fuels are highly-radioactive, so the fuel handling equipment in TEF-P is necessary to be designed as remote-handling system. This report summarizes fabrication and test results of the testing equipment for fuel loading that is one of components of the testing equipment for remote-handling of MA fuels. The testing equipment which had a remote-handling system for fuel loading was fabricated. And the test in combination with the mock-up core was performed. Through the test, it was confirmed to load/take the dummy fuel pin to/from the mock-up core without failure. It was shown that the concept design of the fuel loading equipment of TEF-P was reasonable.
Yamane, Yuichi; Amano, Yuki; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Abe, Hitoshi; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Yoshida, Kazuo; Ishikawa, Jun
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(6), p.783 - 789, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)The release behavior of radioactive materials from high active liquid waste (HALW) has been experimentally investigated under boiling accident conditions. In the experiments using HALW obtained through laboratory scale reprocessing, release ratio was measured for the FP nuclides such as Ru,  Tc, Cs, Sr, Nd, Y, Mo, Rh and actinides such as
Tc, Cs, Sr, Nd, Y, Mo, Rh and actinides such as  Cm,
Cm,  Am. As a result, the release ratio was 0.20 for Ru and 1
Am. As a result, the release ratio was 0.20 for Ru and 1
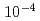 for the FP and Ac nuclides. Ru was released into the gas phase in the form of both mist and gas. For its released amount, weak dependency was found to the initial concentration in the test solution. The release ratio decreased with the initial concentration. For other FP nuclides and actinides as non-volatile, released into the gas phase in the form of mist, the released amount increased with the initial concentration. The release ratio of Ru and NOx concentration increased with temperature of the test solutions. They were released almost at the same temperature between 200 and 300
for the FP and Ac nuclides. Ru was released into the gas phase in the form of both mist and gas. For its released amount, weak dependency was found to the initial concentration in the test solution. The release ratio decreased with the initial concentration. For other FP nuclides and actinides as non-volatile, released into the gas phase in the form of mist, the released amount increased with the initial concentration. The release ratio of Ru and NOx concentration increased with temperature of the test solutions. They were released almost at the same temperature between 200 and 300 C. Size distribution of the mist and other particle was measured.
C. Size distribution of the mist and other particle was measured.